The total market for automotive parts and accessories (HS 87.08) into Sweden was worth US$ 9.8 billion in 2005.
Generally, Sweden offers a good market for high-quality and technically sophisticated automotive equipment. The best sales prospects exist for products within the safety and environment and the related telematics sectors. Swedes are very safety conscious and the automotive manufacturers are known to follow high safety standards. In the aftermarket, a large part of the sales are collision parts, body panels, car glass and headlights.
The import duties are relatively low and vary between 3 and 5 percent for most automotive parts and accessories.
The Commercial Service is available to counsel and assist exporters interested in the Swedish market.
Market Overview
Sweden, with a population of about 9 million, had 4.1 million cars in 2005. This corresponds to one car to every 2.2 people. The number of commercial vehicles was 475,000.
Among the EU15 countries, Sweden has the third oldest car population after Finland and Greece. Four out of ten cars in the Swedish car population are older that 10 years old.
Sales of U.S.-made vehicles are not very high, only 4,709 (incl. vans) in 2005. However, in comparison, U.S. auto parts suppliers are doing well.
The total import of automotive parts and accessories (HS 87.08) was worth US$ 5 billion in 2005. Major supplying countries were Germany (35%), Belgium (8%) and U.K. (8%). US suppliers accounted for 2% percent of the import market.@@Page@@
There are four large-scale automotive manufacturers established in Sweden: Volvo Car Corporation, Volvo Group, Saab Automobile and Scania. These firms manufacture a large range of transportation equipment (cars, buses, trucks, engines, etc.) and have a strong position on the home market. Volvo Car Corporation is owned by Ford and Saab Automobile is owned by General Motors.
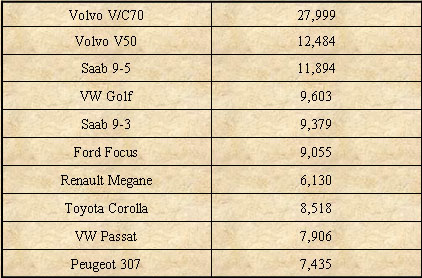
In 2005, the 10 most sold car models were (in number):
In the aftermarket sector, about 60-70% of the turnover is sold through authorized car dealers and garages. The remainder is divided up between independent wholesalers, chain stores and mail-order businesses.
Market Trends
Generally, Sweden offers a good market for high-quality and technically sophisticated automotive equipment.
The best sales prospects exist for products within the safety and environment sectors. Swedes are very safety conscious and the automotive manufacturers are known to follow high safety standards. The sectors include a wide range of products such as products of high strength steel, telematics, emission and alternative energy technology. Both industrial users and manufacturers use the term "environmentally friendly" in marketing. Manufacturers mark parts with material codes and use recyclable materials. In some cases the industry and the state run R&D programs together to support certain clusters.
In the aftermarket, a large part of the sales are for collision parts, body panels, car glass and head lights. Approximately 25 percent of the local distributors’ turnover are for exhaust systems.
Other products that enjoy good prospects are products that relate to the Swedish climate. Examples are engine heaters for the winter and roof boxes for skis. Steering wheels, rims, mirrors and decorations for the exterior of the car also sell well. Extra lights are also popular, especially as it is very dark for 6 months of the year in Sweden. There is also a growing market for truck aftermarket equipment.@@Page@@
Import Market
The statistical data presented in the following table is based on the 2005 import/export statistics and the 2004 (latest available) production statistics for HS 87.08 "automotive parts and accessories" from the Swedish Central Bureau of Statistics. The 2006 figures are unofficial estimates and based on an estimated growth of 5 percent.
US$ Million:
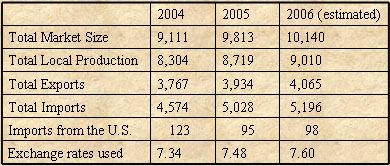
In 2005, the total import of automotive parts and accessories was valued at US$ 5 billion, which is an increase of 10 percent compared to the year before.
Germany is by far the largest supplying country to the automotive parts and accessories market with a 35% share of the import market. A large number of German firms are active in Sweden, among these are Robert Bosch, Man Filter, Isringhausen (seats for trucks), Hella (electrical lighting), Boge (shock absorbers), VDO (instrument panels and audio equipment) and Sachs (couplings, transmissions). Other well known brands are Eberspächer, Brose and Borgers.
Another important supplying country is the United Kingdom (8%) with a number of leading firms such as Lucas (starter motors). Belgian suppliers (8%) have also gained a strong foothold on the Swedish market. France (Valeo, Faurecia), Japan (KYB, Showa) and Poland are also important suppliers to Sweden.
US suppliers of automotive parts and accessories account for about 2% of the import market. The figure does not capture much of the U.S. parts that are transshipped via major European ports (e.g. Rotterdam). If these were included, U.S. imports could probably be more than twice the official figure. Areas where US suppliers are doing well are within brake systems, steering systems, body parts and gearboxes/transmissions. Car care products and automotive chemicals are other segments where U.S. firms are strong.@@Page@@
Some of the major US companies exporting to Sweden (or producing in Sweden) are:
Arvin Meritor
Champion Ignition Products
Clevite
Collins & Aikman
Dana Corporation
Delphi Automotive System
Federal Mogul Corp.
Gates Rubber Co
Johnson Controls
Lear Corporation
McCord Gasket Corp.
Monroe Auto Equipment Co
Moog Automotive, Div.
Standard Motor Products, Inc.
Tenneco
Walker Mfg. Co
Competition
As regards the OEM market, Swedish-based suppliers account for some 30 per cent of the Swedish motor vehicle manufacturers’ total purchasing volume, with an approximate value of US$ 2.5 – 3.1 billion.
The supplier companies are a heterogeneous group and range from small enterprises with 20-30 employees to large corporations with several thousand employees in Sweden and abroad.
The Swedish supplier cluster includes a number of large companies like Autoliv, SKF, Haldex and SSAB. In addition many system suppliers, among them Delphi, Getrag, Visteon, Johnson Controls, Tenneco, Valeo, Robert Bosch and Bentley have established operations and subsidiaries in Sweden.
In recent years, a great deal of responsibility for manufacturing and product development has been transferred from the motor vehicle manufacturers to system suppliers. The market for engineering and design services has grown and examples of large consultancy firms are Semcon, Caran Sigma and Teleca.
Electronic components suppliers have become an important segment of the supplier cluster in Sweden. Sweden currently holds a strong position in the fields of telematics and active safety technology.@@Page@@
The Swedish component manufacturers are, together with Norwegian and Finnish companies, organized in an industry association called "Scandinavian Automotive Suppliers" with about 300 member companies. The companies supply a wide variety of components and systems to the Swedish automotive manufacturers as well as to other suppliers. Foreign companies with local offices are also members of the association.
The aftermarket sector is estimated to be worth US$ 2.7 billion. The largest share has spare parts and accessories (US$ 1.5 billion) followed by bodywork and paint (US$ 0.7 billion). The market for wheels and tires is valued at US$ 0.5 billion.
The specialist retail sector has over 400 spare parts stores with sales to motorists and workshops, and represents an estimated 90 per cent of the brand-independent market. Sweden’s four largest spare parts players are Mekonomen, the Meca group, the KG Knutsson group and APE Fordonskomponenter. These players cover most vehicle brands, and their customers are brand-independent workshops.
There are over 6,000 vehicle workshops in Sweden, of which about 1,000 are branded workshops.
There is a cluster of discount players like Auto-Trak in the U.S., which are mainly targeted at the consumer with Biltema being the major one. Another important chain is Micro, which aims at the do-it-yourself market. The traditionally large do-it-yourself market is, however, getting smaller as new cars become more complex.
End Users
In the OEM sector, the end users are the vehicle manufacturers. As stated above, there are four domestic manufacturers of motor vehicles in Sweden:
Volvo Car Corporation manufactures passenger cars and specializes in the upper segment of the market. In 2005, the company manufactured 447,000 cars. Volvo Car Corporation was purchased by Ford in 1999.
The Volvo Group manufactures trucks, buses and marine, industrial and aircraft engines. In 2005, the company manufactured 204,000 trucks (including Volvo-owned Mack and Renault trucks) and 9,000 buses. A separate company within the group is Volvo Construction Equipment. It is one of the world's leading manufacturers of wheel loaders, excavators and articulated haulers and the second largest truck producer in the world.
SAAB Automobile, which makes passenger cars only, manufactured 121,000 cars in 2005. The company is wholly owned by General Motors.
Scania manufactures trucks, buses and marine and industrial engines. Scania manufactured 53,000 trucks and 6,100 buses in 2005. Volkswagen is a major shareholder in Scania.
From an international perspective, Swedish automotive manufacturers produce relatively few passenger cars, accounting for only 1.5% of world production. In terms of heavy vehicles over 16 tons, however, Swedish manufacturers are among the largest in the world. One fifth of heavy trucks sold in the world in 2005 were manufactured by either Volvo (incl Mack and Renault) or Scania and Swedish companies manufacture more diesel engines than any other country in the world.@@Page@@
Purchasing from U.S. suppliers by the Swedish OEMS is a collaboration of U.S. and Swedish offices. The policy during recent years has been to work closely with suppliers that develop and manufacture complete modules and systems. The result is that the number of first tier suppliers is being reduced.
The systems suppliers are encouraged by the car manufacturers to establish plants near the assembly facilities. Examples of this are the supplier parks adjacent to Volvo's main plant in Gothenburg where 15 foreign-owned subcontractors are located.
US exporters interested in selling to the system suppliers are recommended to contact the "Scandinavian Automotive Suppliers" in the first instance. The association has advised that it will assist in establishing contacts with its members.
As regards the aftermarket sector, the dominant organization is the Association of Swedish Wholesalers of Automotive Parts and Accessories. The members companies of this organization provide access to the manufacturing sector of vehicles as well as to the entire aftermarket sector.
Market Access
In order to sell products on the Swedish market, U.S. exporters must meet the CE mark requirements applicable to their products. The CE mark certifies that the products have met the health, safety and environmental requirements of the EU to ensure consumer and workplace safety. Once a manufacturer has earned a CE mark (some cases self-certify others require certifying agents), it may affix the CE mark to its product, and then the product may be marketed throughout the EU. Further information can be found in http://www.ita.doc.gov/td/tic/ce_mark/ceintro.htm.@@Page@@
The import duties are the same as those of the other countries in the European Union and vary between 3 and 5 percent for most automotive parts and accessories. Potential exporters can check possible duty rates on-line at the following web site of the Swedish Customs: http://taric.tullverket.se.
The value added tax (VAT) is 25 percent on all products (imported as well as locally produced) and is paid at the port of entry.
Sweden uses the metric system. All product literature should be expressed in metric terms.
Market Entry
As a rule the Swedish vehicle manufacturers prefer to deal directly with foreign suppliers rather than going through agents.
As regards the aftermarket, it is more common to work through importers/agents or wholesalers. The products are thereafter sold through dealers, car part stores, garages and gas stations. Mail order firms also play an important part in the distribution system. About 60 – 70% of the sales go through authorized car dealers and garages.
Of specific interest are the European Commission “Block Exemption” rules, which were introduced in 2002. The rules were designed to create more competition in the servicing and repair market leading to lower costs for consumers. Independent garages will have much greater access to technical information, including diagnostic equipment and software. “Original” parts will be available to authorized repairers directly from the suppliers.