The global intelligent driving sector has moved beyond the "technology verification" phase, entering a critical stage of mass deployment.
According to the "Advanced Driving Assistance System (ADAS) Industry Report (2025 Edition)" by Gasgoo Institute, the penetration rate of L2-level and above ADAS features in domestic passenger vehicles reached 57% between January and August this year. As prices dip into the 100,000-yuan range, equal access to driver assistance is accelerating. Highway NOA penetration is nearing 20%, while city NOA sits around 4%. Notably, models standard-equipped with city NOA have already fallen below the 150,000-yuan mark, suggesting that high-level driver assistance adoption will only climb further.
Against this backdrop, the Huawei Qiankun Media Day provided a key vantage point. The progress and strategic layout revealed by Huawei's intelligent driving business offer a crucial window into where the industry's technology is heading.
As a top-tier player, every move by Huawei Qiankun Intelligent Driving reflects the path Chinese smart car companies are navigating between technological autonomy and ecosystem synergy.
Objectively speaking, Huawei Qiankun's full-stack self-research route stands as a typical example of China's intelligent automotive industry shifting from "technology following" to "independent innovation."
Jin Yuzhi, CEO of Huawei's Intelligent Automotive Solution BU, announced at the event that by the end of 2026, models equipped with the Huawei Qiankun intelligent driving system will exceed 80, with a cumulative installation volume expected to reach roughly 3 million units.
Currently, the Huawei Qiankun Intelligent Driving system is not only applied to products under the Harmony Intelligent Mobility Alliance but has also secured technical adoption from major automakers including BYD, Dongfeng, Audi, FAW, Changan, GAC, and BAIC. In terms of product mix, relevant models now span sedans, SUVs, MPVs, and off-road vehicles.
Huawei's technical advancements have driven overall industry progress and indirectly accelerated the convergence of technical standards. Yet, the challenges of cost control and ecosystem adaptation brought by a full-stack approach remain issues Huawei—and the industry as a whole—must face together.
Path Selection: Full-Stack Self-Research
"We adhere to the multi-sensor fusion technical route. Through a vertically integrated architecture, we guarantee system safety and iteration efficiency in every aspect, from chips to the underlying operating system," Jin Yuzhi told media outlets including Gasgoo, outlining the core logic behind Huawei's full-stack self-research strategy.
With full-stack self-research as its strategic pivot, Huawei Qiankun has built a complete technical system covering core links such as ADS, the Harmony cockpit, vehicle control, and vehicle cloud services.
This choice was not accidental; it was a rational judgment based on the characteristics of intelligent driving technology and the current stage of industry development.
Fundamentally, the core demand for intelligent driving is "safety and reliability." Compared to the "patchwork mode" reliant on multiple suppliers, full-stack self-research not only resolves system compatibility and response efficiency issues but also builds competitiveness in safety and iteration speed.
According to official Huawei data, driving a vehicle equipped with Huawei Qiankun Intelligent Driving ADS—whether in manual or assisted mode—significantly improves the average safe driving mileage compared to the Chinese average (estimated).
Behind this advantage lies the deep synergy of core components: chips, algorithms, and sensors.
Huawei's breakthroughs in technical details further highlight the innovative value of the full-stack route.
In the technical landscape of intelligent driving, reliance on high-definition maps was once a "shackle" for many systems. While HD maps offer detailed road information, they suffer from slow updates, limited coverage, and high costs. Huawei ADS 2.0 made a bold innovation by taking a different path, leveraging GOD 2.0 (General Obstacle Detection Network) and RCR 2.0 (Road Topology Reconstruction Network) technologies to drastically reduce reliance on HD maps. This technology has since become a core standard for high-end intelligent driving.
The upcoming Huawei Qiankun Intelligent Driving ADS 4.1, for the Harmony Intelligent Mobility Alliance lineup, centers on functional optimization across multiple dimensions.
According to official introductions, ADS V4.1 includes several safety enhancements. It adds support for the eAES "anti-sandwich" function, which can predict the risk of approaching vehicles from behind to effectively prevent rear-end collisions. eAES performance has been further strengthened for all-weather safety protection. The system also optimizes human driving assistance capabilities, providing more precise escort assistance on sharp curves and at intersections. If the driver suddenly becomes incapacitated, the system automatically pulls over and calls for rescue. Hands-off status triggers real-time reminders, with a safety pull-over mechanism triggered after a timeout. Even in extreme situations like a tire blowout during manual driving, the system can maintain composure, assisting the vehicle to drive stably.

Image source: Gasgoo on-site photography
Looking at industry technical evolution, Huawei's WEWA architecture—composed of the cloud World Engine (WE) and the on-vehicle World Action Model (WA)—represents a typical generative end-to-end architecture.
Specifically, the cloud World Engine (WE) uses a diffusion generation model to simulate extreme scenarios, generating a density of difficult cases 1,000 times that of the real world; it has completed 600 million kilometers of L3 simulation verification. The on-vehicle World Action Model (WA) employs a MoE (Mixture of Experts) architecture to achieve full-modal perception and precise scene invocation. This architecture cuts end-to-end latency by 50%, boosts traffic efficiency by 20%, and reduces heavy braking rates by 30%.
This evolutionary path aligns with the surging "Physical AI" trend, efficiently solving the long-tail scenario coverage challenge by combining high-fidelity virtual simulation with real-world road test data.
In May 2025, the Harmony Intelligent Mobility Alliance MAEXTRO S800 became the first mass-produced model equipped with ADS 4, followed by the VOYAH FREE and Dongfeng M-Hero M817. As of January 2026, the actual usage mileage of Huawei Qiankun Intelligent Driving ADS reached 7.283 billion kilometers, providing massive data support for algorithm optimization.
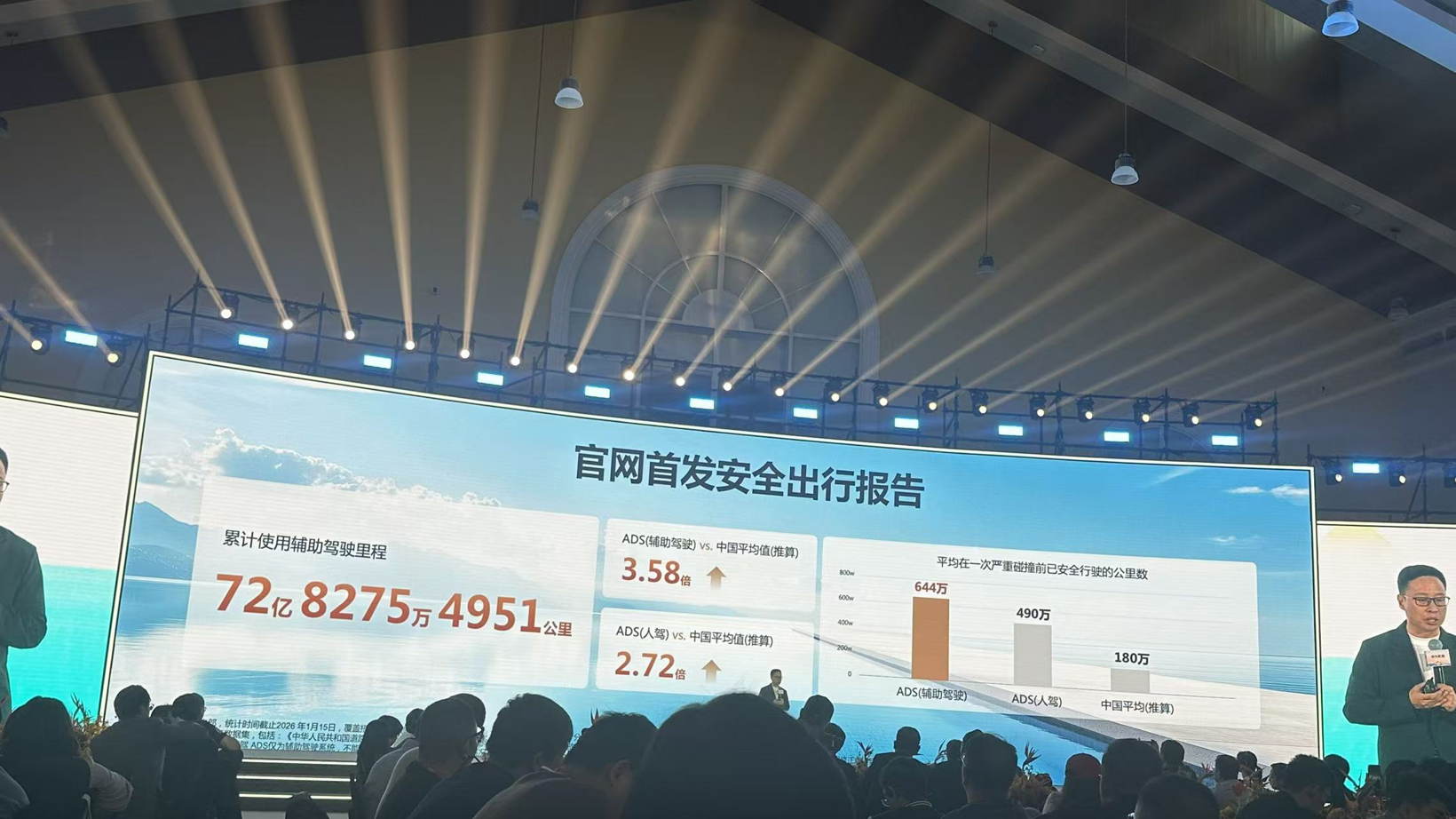
Image source: Gasgoo on-site photography
It is worth noting that Huawei's technical route is not the industry's only solution, but rather an important branch within a diverse technological ecosystem.
The industry currently forms three major camps: "full-stack self-research," "algorithm self-research + hardware outsourcing," and "full-stack outsourcing + secondary development." Different routes have their adapted scenarios.
Regarding automakers emphasizing full-stack self-research, Horizon Robotics Vice President Lu Peng stated in an interview: "In the end of this industry, there will certainly be some who do Apple, but the majority will do Android. Apple will always be the minority. Doing Apple means self-researching everything; everything is your own. What does Android do? Like Horizon, we 'eat from a hundred families,' serving so many automakers to achieve scale, and our investment is focused. Automakers have to pay attention to too many things; our entire company focuses on just one thing: getting autonomous driving right. On this basis, the majority of the market should still be provided by suppliers like us."
This very difference constitutes the driving force for industry technical iteration. Huawei's full-stack practice provides the industry with a model of "end-to-end controllability," while other routes explore possibilities in balancing cost and efficiency.
Intelligent Driving Upgrade: Building Trust through Safety
In 2024, there were 260,000 road traffic accidents nationwide, resulting in 59,000 deaths and 254,000 injuries—an average of 857 casualties per day.
Jin Yuzhi emphasized that as the penetration of driver assistance increases, safety is paramount in the move toward conditional autonomous driving, because vehicle safety concerns every individual and family.

Image source: Gasgoo on-site photography
The ADS 4.1 omni-directional anti-collision system CAS 4.0, paired with eAES 2.0 enhanced automatic emergency steering assistance, can accurately identify irregular obstacles and actively avoid risks—such as construction barrels suddenly appearing on highways or cattle and sheep darting out on rural roads. The newly added AEB animal recognition function specifically targets rural scenarios common during the Spring Festival return trip, resolving the pain point of slow response to "non-standard obstacles" by previous intelligent driving systems.
Even more reassuring is the assisted driving blowout stability control 2.0. Even if a front tire blows at 130 km/h, the system can stabilize the vehicle body and guide it to pull over. Compared to the old version, which could only handle low-speed blowouts, this upgrade maxes out high-speed driving safety levels. Additionally, functions like driver incapacitation automatic pull-over and hands-off timeout safety parking add an extra layer of fallback protection to "semi-autonomous driving."
China averages one serious collision accident (airbag deployment or safety mechanism trigger) every 1.8 million kilometers. After equipping the ADS system, this figure becomes one every 4.9 million kilometers in human driving mode; in assisted driving mode, safety is 3.58 times the Chinese average.
Jin Yuzhi noted that user reputation improved following the upgrades to ADS 3.3 and 4. Although some users feel ADS 4 is more cautious, actual safety is 50% higher than ADS 3.3, and the usage ratio in urban areas has also risen.

Image source: Gasgoo on-site photography
Notably, in 2025, the China Automotive Engineering Research Institute (CATARC), a national authority, spearheaded a high-specification practical test for driver assistance safety. In this authoritative test covering six mainstream models, the SAIC H5 under the Harmony Intelligent Mobility Alliance brand, equipped with Huawei Qiankun Intelligent Driving ADS 4, smoothly passed seven basic scenarios and actively volunteered for additional extreme complex scenario tests, demonstrating safety redundancy capabilities beyond its class.
It must be objectively stated that the industry has not yet formed a unified standard for intelligent driving safety data statistics, and statistical criteria vary among different enterprises. This is not a Huawei-specific case but a problem the entire industry needs to solve together. The value of Huawei's practice lies in providing a reference for building an industry trust system by opening up its data statistical logic and accepting third-party testing.
Huawei's exploration in safety technology has also driven the improvement of industry standards.
The "Safety Requirements for Intelligent Connected Vehicle Combined Driving Assistance Systems," which it participated in drafting, was declared a project on March 22, 2024, with a 22-month cycle. On June 4, 2025, the standard was opened for public comments for the first time via the National Standard Information Public Service Platform.
This standard defines a combined driving assistance system as a system composed of hardware and software that continuously executes the vehicle's lateral and longitudinal motion control during dynamic driving tasks within its design operational domain, and possesses hardware and software capable of partial object and event detection and response appropriate to the executed motion control. It applies to M and N class vehicles equipped with L2 combined driving assistance systems, covering technical requirements such as motion control capability, functional safety, driver state monitoring, and system boundaries and response.
As an expert told Gasgoo, "The safety practices of leading enterprises often become implicit industry standards. Huawei's value lies in translating safety concepts into implementable technical solutions and process norms, which has positive significance for the improvement of the industry's overall safety level."
Diversified Cooperation and the Symbiotic Logic of Ecosystem Value
Competition in the intelligent vehicle industry is no longer between single enterprises or single technologies, but between ecosystems.
Huawei's "full-stack solution + open cooperation" model aims to balance "technology empowerment" with "OEM autonomy." It provides automakers with full-chain intelligent capabilities from chips to cockpits, while preserving their autonomy in product definition, exterior design, and brand operations.
In terms of cooperation models, Huawei's ecosystem layout presents a "layered adaptation" characteristic. For deep cooperation brands like AITO and Avatr, it adopts a full-stack solution to achieve deep synergy in intelligent driving, cockpits, and vehicle control. For traditional luxury brands, it provides customized services for core cockpit or intelligent driving modules based on their technical needs, retaining their own technical accumulation and brand characteristics.
This model not only leverages the integration advantage of Huawei's full-stack technology but also respects the independent demands of automakers, avoiding the industry pain point of "technological homogenization."
Currently, centering on the vehicle ecosystem, Huawei provides intelligent solutions for automakers, empowering Qiankun Intelligent Driving, Harmony Cockpit, Qiankun Vehicle Control, Qiankun Vehicle Cloud, and Qiankun Automotive Optics. Cooperation brands include Avatr, M-Hero, Qijing, Yijing, Hongqi, VOYAH, DEEPAL, HYPTEC, and Audi, achieving full-stack integration.

Image source: Gasgoo on-site photography
Take the Yijing brand, jointly created by Dongfeng and Huawei Qiankun, as an example. Based on Huawei technology, it has developed family-specific intelligent driving functions, forming a differentiated competitive advantage. Huawei opened core technologies such as the Qiankun Intelligent Driving ADS 3.0 system and Harmony Intelligent Cockpit 4.0. Its first model will be equipped with the latest generation of Qiankun Intelligent Driving, Harmony Cockpit, Qiankun Vehicle Control, Automotive Optics, and Vehicle Cloud, making it one of the models with the highest Huawei technology integration.
Jin Yuzhi mentioned that the first Yijing vehicle is a full-size SUV, while the first Qijing vehicle is positioned as a shooting brake coupe. Both new cars will make their debut at the 2026 Beijing Auto Show on April 24.
For the user-facing ecosystem, Huawei centers on Qiankun Intelligent Driving, the Qiankun APP, and the Harmony car machine APP to provide usage ecosystem applications such as parking, car washing, and charging. These are interconnected with the Harmony OS ecosystem, enabling convenient services under autonomous driving in the future.
Since its release in 2025, the Huawei Qiankun APP has surpassed 1 million downloads, with 660,000 users. Core functions cover scenarios such as model comparison, user feedback, and vehicle control services. Its distinctive feature lies in breaking through the ecological synergy of Huawei phones and tablets, realizing seamless flow between "car machine and mobile," which enhances the user's all-scenario vehicle experience.
From an industry comparison perspective, while the user activity of the Huawei Qiankun APP is lower than some vertical brand tools, this data already reflects the integration value of a cross-brand ecosystem given its attribute of covering multi-brand models.

Image source: Gasgoo on-site photography
In the future, as services like parking, car washing, and charging are further integrated, its ecosystem closed-loop capabilities will continue to improve.
Conclusion:
The development path of Huawei Qiankun Intelligent Driving is a microcosm of independent innovation in China's intelligent automotive industry.
Its full-stack self-research route has brought technological breakthroughs and enhanced industrial value, but it also faces realistic challenges such as cost, penetration, and globalization. This state of "coexisting advantages and challenges" aligns with the objective laws of technological innovation and industrial development.
From an industry perspective, Huawei's practice provides a reference model of "technological autonomy + ecosystem synergy" for Chinese intelligent driving enterprises, promoting the improvement of industry technical standards and safety levels.
Looking ahead, competition in the intelligent vehicle industry will be a comprehensive contest of technological strength, ecosystem capability, and cost control. Whether Huawei can solve the puzzle of large-scale development while maintaining its technological edge hinges on its ability to grasp the rhythm of "innovation and balance."
For the industry as a whole, the coexistence and benign competition of diverse technological routes are the core driving force for high-quality industrial development. Huawei's exploration and growth will continue to provide important reference value for the industry.