On September 29, 2024, NIO Inc. announced that it has entered into definitive agreements for strategic investments in its subsidiary NIO Holding Co., Ltd. (NIO China). The strategic investors—Hefei Jianheng New Energy Automobile Investment Fund, Anhui Provincial Emerging Industry Investment Co., Ltd., and CS Capital Co., Ltd.—will inject 3.3 billion yuan in cash, subscribing to newly issued shares of NIO China. Simultaneously, NIO will invest 10 billion yuan, maintaining an 88.3% controlling equity interest after the transaction is completed.
Hi, welcome to Gasgoo. In this episode of “Wheels of Change: Stories of Chinese Auto Giants,” let’s talk about NIO.
NIO, a Chinese Brand into the High-end Vehicle Market
In 2014, 40-year-old Li Bin made the decision to invest his entire fortune of 150 million dollars in the new energy vehicle industry and founded the NIO brand based on his optimistic view of its future development. Prominent figures from the Internet and technology sectors, including JINGDONG's Liu Qiangdong, Tencent's Ma Huateng, and Xiaomi's Lei Jun, have also invested in the company.
At its inception, NIO did not initially enter the mass market. Instead, it chose to gain a foothold in the industry by breaking through in a different way. In 2014, NIO made its debut in Formula E, the global electric street racing, and won the championship, gaining notable international recognition and showcasing its technology and innovation to the world.
In 2015, NIO unveiled its first electric supercar, the EP9. This vehicle is the foundation of the company's strategy to establish itself as a technology leader in the electric vehicle industry. Without disappointing the expectations, the EP9 set a new lap record at Germany's Nürburgring track, shocking the entire European and American markets.
By participating in top-level electric formula racing, NIO has enhanced the team's R&D capabilities and technical resources, while raising its profile. As a new entrant to the electric vehicle market, NIO has quickly established a high-end brand image.
In November 2016, NIO held its first launch event in London, UK. The company unveiled its English brand "NIO," a new logo, and the EP9 battery electric supercar. Notably, the first batch of EP9s was limited to six units, not available for sale, and given to the initial founding investors, including NIO founder and chairman Li Bin, Tencent chairman and CEO Ma Huateng, JINGDONG CEO Liu Qiangdong, Autohome founder Li Xiang, Xiaomi founder Lei Jun, and Hillhouse Capital founder Zhang Lei.
In December 2017, NIO launched its first all-electric SUV, the NIO ES8, with two versions: the Base and Premier Edition trims, priced at 448,000 yuan and 548,000 yuan, respectively. In addition, the price could be reduced by an additional 100,000 yuan by opting for the battery leasing option. The NIO ES8 featured a 2+3+2 seating layout, a length of over 5 meters and a wheelbase of over 3 meters. By the end of 2018, NIO had delivered 11,348 ES8s, exceeding the initial target of 10,000 units.
In August 2018, NIO submitted its IPO prospectus to the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), marking the start of the listing process. On September 12, 2018, NIO successfully listed on the New York Stock Exchange in the U.S., raising approximately 1 billion U.S. dollars and becoming the first Chinese new energy vehicle company to go public in the U.S. From inception to listing, NIO achieved this milestone in just four years.
In December 2018, NIO launched the new mid-size pure electric SUV, the NIO ES6, which featured a five-seat layout and was available in three versions: the Standard, Performance and Premier Edition trims. The vehicle accelerated from 0 to 100 km/h in 4.7 seconds, had an NEDC range of up to 510 kilometers, and was available for between 358,000 and 548,000 yuan before subsidies. Based on its price and performance, the ES6 was positioned as a volume model, and it did indeed boost NIO's sales.
According to the data, from the official delivery in June 2019 to the end of the year, NIO delivered 11,433 units of the ES6. Combined with the 9,132 units of the ES8 delivered, NIO's total vehicle deliveries in 2019 reached 20,565 units, an 81% year-on-year increase. By the end of 2019, NIO had achieved a remarkable cumulative delivery of 31,913 units, ranking first among Chinese new energy vehicle startups.
However, NIO's record deliveries coincided with operational challenges and mounting losses. In 2019, NIO faced stagnant funding, the departure of founding shareholders, and the resignation of senior executives. These challenges, coupled with product issues such as fires and recalls and the withdrawal of subsidies for new energy vehicles, brought the company to the brink of bankruptcy. Li Bin was even dubbed "the unluckiest person in 2019."
Fortunately, by the end of April 2020, NIO secured 7 billion yuan of state capital investment from Hefei, which enabled NIO to temporarily overcome its funding difficulties. By the end of 2020, NIO's total market value reached $72.84 billion, surpassing traditional giants BMW and Daimler to become the top player in the new energy vehicle market. Li Bin has changed from being "the unluckiest person in 2019" to "the most successful person in 2020".

Photo credit: NIO
From its founding in November 2014 to 2023, NIO has released eight models, including ET series sedans (ET7, ET5 and ET5T), ES series SUVs (ES8, ES7 and ES6) and EC series coupe SUVs (EC7 and EC6), with most models priced above 300,000 yuan, targeting the high-end market.
All-in on R&D: Seizing the Once-in-a-Century Opportunity
Throughout its development, NIO has emphasized a user-first approach while making substantial investments in research and development (R&D). NIO has engaged in a comprehensive range of activities, such as battery production, chip R&D, building battery swap stations, and even launching its first smartphone, the NIO Phone. Despite the ongoing debates about the scope of R&D and the roadmap of energy supplementation technology, NIO's continued investment is undeniable.
According to NIO's financial reports, NIO had invested a total of 43 billion yuan in R&D by the end of 2023, with more than 10 billion yuan in both 2022 and 2023. In the first quarter of this year, NIO's R&D investment reached 2.86 billion yuan.
Why did NIO develop in-house?
When NIO was just founded, the goal for the ES8 was to achieve 0-100 km/h acceleration one second faster than the Tesla Model X (4.5 seconds). NIO's R&D team then conducted a global search for electric motor suppliers, but only Japan's FUJI met the requirements. Notably, this supplier is also Tesla's exclusive supplier. This led NIO to realize the need to establish a comprehensive in-house technology R&D system and battery swap service network to ensure the brand's core competitiveness and facilitate continuous product iteration in line with target expectations and market conditions.
In other words, in-house R&D is the only way for NIO to achieve its goal of being an independent and high-end Chinese car brand.
Qin Lihong, co-founder of NIO, also said that the intelligent electric vehicle industry is facing a once-in-a-century transformation, and only by going all-in on R&D can NIO avoid missing this rare opportunity.
At the "2023 NIO IN Innovation and Technology Day" held on September 21, 2023, NIO showcased its achievements and strategies in the field of technology, such as self-developed chip, NIO phone, SkyOS, NOP+, and other cutting-edge technologies, thus reinforcing its "technology-driven" brand image.
After nearly nine years of automobile manufacturing, NIO has fully engaged in self-research in 12 core technology categories, including intelligent driving, intelligent cockpit, intelligent energy, panoramic connectivity, vehicle-wide operating system, chip and in-vehicle intelligent hardware, vehicle engineering, battery system, electric drive and high-voltage system, intelligent manufacturing, artificial intelligence, and global digital operation.
As an illustration, chips and in-vehicle intelligent hardware represent a key area of NIO's self-research. NIO's first in-house developed chip, Yangjian NX6031, is a LiDAR master controller chip. The chip began full integration into NT2.0 models starting in October 2023, with the mass production of Seyond's LiDAR.
In addition to the "Yangjian" chip, NIO’s chip team has also focused on developing advanced chips with higher process technology, such as autonomous driving chips. Before developing its own chip, NIO was heavily involved in the development of hardware for autonomous driving, intelligent cockpits and automotive electronics, such as the Orin-based ADAM supercomputing platform and the NOMI Mate intelligent voice assistant.
While chip development, autonomous driving and NIO Phone are highlights of NIO's research achievements, basic research and development remains a top priority. As a new player in the automotive industry, NIO has been engaged in several fundamental research and development activities, including the SkyOS vehicle-wide operating system mentioned at the 2023 NIO IN event. SkyOS comprises several layers, from user applications to middleware, the operating system kernel, and the Hypervisor.
The debut of NIO's SkyOS marks an important step for China's intelligent vehicle operating systems. NIO has already mass-produced parts of the SkyOS framework on its first two generations of technical architecture, NT1.0 and NT2.0. NIO is currently fully engaged in the development of the NT3.0 platform, which will enable the full-fledged mass production of SkyOS.

Photo credit: NIO
In 2023, NIO released its high-end model, the ET9, equipped with four-wheel independent suspension. Each suspension has a motor for the air springs that allows the suspension to be adjusted more than a thousand times per second, combined with LIDAR that uploads road conditions to be adjusted at any time.
For example, the suspension can be adjusted in real time before the vehicle hits a speed bump, ensuring maximum comfort for the driver and passengers. This exceptional functionality is a comprehensive reflection of NIO's self-research in electric drives, chips and intelligent driving.
NIO's R&D efforts also focus on industry clusters and supply chain collaboration, integrating components and upstream technology for efficient synergy. NIO has now established a comprehensive global R&D and production system, with global and Chinese headquarters located in Shanghai and Hefei, respectively. Currently, NIO’s Chinese factories mainly produce vehicle manufacturing, battery packs and electric drive assemblies.
NIO is the world's first automotive company listed in the U.S., Singapore and Hong Kong, China, completing its global R&D layout in Europe, Asia and the Americas. The diverse expertise of top talent in different regions provides a global perspective that informs R&D decisions.
Qin Lihong mentioned that NIO currently employs over 10,000 R&D professionals worldwide dedicated to digitalization, intelligence and software development. Moreover, NIO has obtained and applied for more than 8,600 patents worldwide, of which more than 1,500 are related to battery swapping.
NIO's global R&D layout and large R&D investment are crucial to its future growth and success. With the full integration of automotive technology and the long-term cost reduction effects of early investments, NIO's image as both a service-oriented and technology-driven company is solidified.
However, the substantial R&D investment is also a reason why NIO remains loss-making. NIO's R&D projects are costly and may not yield immediate results. Li Bin believes that NIO should use R&D investment for long-term gross profits. Although there are challenges, NIO's commitment to R&D will not waver. Technology is a primary productive force and the essential guarantee for NIO to compete in the increasingly fierce intelligent electric vehicle market.
In addition to R&D, NIO Capital has invested in numerous companies and technologies related to its supply chain. NIO Capital is positioning itself as a connector in the new energy vehicle industry, creating a wide alliance-style moat for NIO.
In terms of investment strategy, NIO Capital focuses on three key sectors: intelligent transportation, new energy and intelligent manufacturing, concentrating on the industrial transformation brought about by low-carbon and digital technologies and model innovation, especially the opportunities in the new energy, automotive and deep technology sectors.
NIO Capital has invested in more than 70 companies in the battery, LiDAR and other sectors, such as CATL, Ronbay Technology, UW Laser, Tuhu Automotive Service, Momenta, Inceptio Technology, Pony.ai, Black Sesame Technologies and so on.
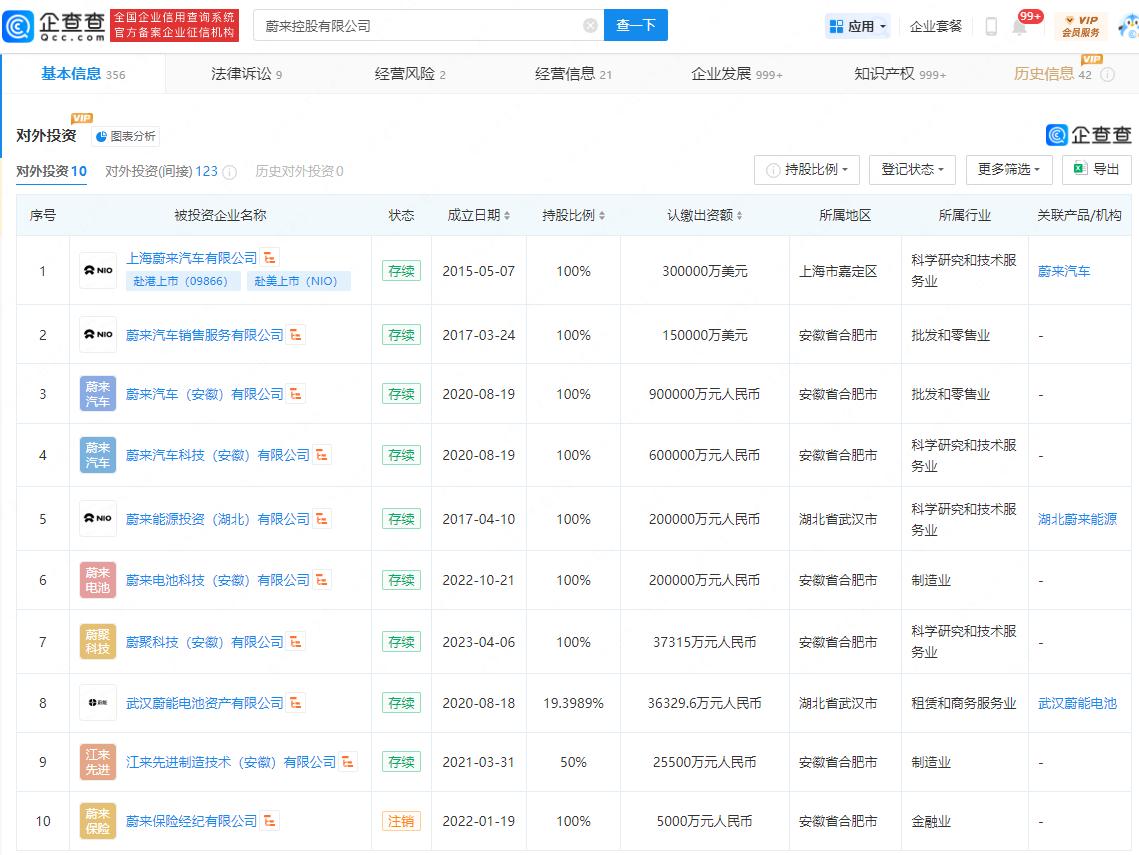
Photo credit: Qichacha
NIO Holding Co. currently holds direct interests in 10 companies engaged in automobile sales, energy investment, automobile batteries, advanced manufacturing, etc. Additionally, NIO Holding indirectly controls hundreds of companies, most of which are sales, service and energy companies located in various cities in China.
NIO’s "Moat": Energy Replenishment Ecosystem:
Li Bin is an idealist.
His vision for NIO is to create a Chinese premium brand that can compete with BBA (BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Audi) and even Porsche. At the same time, he aspires to build a comprehensive energy replenishment network that makes charging more convenient than refueling. Although NIO still has room to grow in terms of sales, the goals he has been striving for are gradually being realized.
In the electric vehicle industry, NIO is dedicated to offering customers a seamless and comprehensive experience. This commitment is evident in its high-end vehicle design, comprehensive battery charging and swapping network, and efficient service system. NIO aims to set new service standards in the electric vehicle industry through its innovative service model.
NIO is the first new electric vehicle startup in China to establish a battery swapping network. Since the first battery swapping station was built in Shenzhen's Nanshan Technology Park in 2018, NIO has established more than 2,000 battery swapping stations. This large capital investment was one of the main reasons for NIO's continued financial losses. The profitability of the battery swapping stations has raised concerns and even attracted the attention of short-selling firms.
In the early days, given the small number of NIO vehicles on the road and the decision to offer a lifetime free battery swapping policy, the battery swapping system seemed like a user-friendly moat, but in reality it became a heavy burden.
As a stalwart in the battery swapping mode, NIO is beginning to see positive developments. NIO has partnered with numerous automakers, including Changan, Geely, JAC, Chery, Lotus, GAC, FAW and others in the field of battery swapping. Furthermore, NIO has also cooperated with prominent energy and power companies such as Sinopec, CNOOC, Shell, State Grid, China Southern Power Grid Company, Wenergy Group, etc. to further expand its battery swapping network.
In recent years, the battery swapping mode has also received significant support from the Chinese government, as evidenced by documents such as the New Energy Vehicle Industry Development Plan (2021-2035), the "implementing Opinions on Further Enhancing the Service Guarantee Capacity of Charging and Battery Swapping Infrastructure" and the Notice on Starting the Pilot Application of New Energy Vehicle Battery Swapping Mode, which have promoted the construction of battery swapping networks and the formulation of related standard systems.
In March of this year, NIO adjusted the price of its BaaS battery rental service: the monthly rental fee for the 75kWh battery pack was reduced from 980 yuan to 728 yuan, and the 100kWh battery pack was reduced from 1,680 yuan to 1,128 yuan. In addition, the corresponding rewards were refunded for each rental order. The price adjustment was both a response to the intensifying price war in the market and an effort to attract more users to join the “battery swapping ecosystem”.
From a cost perspective, although NIO has never disclosed the specific construction and operating costs of its battery swapping stations, industry analysts estimate that the cost of NIO's first-generation battery swapping station was 3 to 3.5 million yuan, the second-generation station was about 2 to 2.5 million yuan, and the third-generation station was reduced to 1 to 1.5 million yuan. With the advancement of technology and infrastructure, the cost of NIO's battery swapping station has been gradually reduced, providing a basis for the recent price adjustments of the BaaS service.
According to the report, NIO’s battery swapping stations in Shanghai are already profitable. As NIO continues to expand its customer base and increase car sales and the frequency of users’ battery swaps, NIO’s battery swapping business is expected to reach break-even or even overall profitability.

Photo credit: NIO
NIO’s sub-brand NioPower is dedicated to providing flexible charging and battery swapping solutions. NIO believes that charging and swapping are not mutually exclusive, but can be complementary, offering options for charging, swapping and upgrading to meet different user needs.
For instance, NIO's battery swapping stations are an important part of its service network. NIO has more than 2,380 battery swapping stations across China, which can replace an EV's battery in just a few minutes, greatly improving travel efficiency. This service is particularly popular with frequent long-distance travelers, as it virtually eliminates the common concern of range anxiety among EV users.
Moreover, NIO offers tailored solutions for battery upgrades with standardized battery packs. The cost of swapping a battery is typically between 30 and 40 yuan per day, about the price of a cup of coffee. A small battery is typically used for city commuting, while a large battery is used for vacation travel. Flexible upgrades can be provided to meet the needs of long-distance travel.
As of June 13, 2024, NIO has built 2,432 battery swapping stations and 22,633 chargers across China, including 804 highway battery swapping stations and 1,650 highway chargers, making it the automotive brand with the most extensive battery swapping and charging infrastructure in the country. In addition, NIO’s first batch of fourth-generation battery swapping stations are now operational, supporting multi-brand and multi-model autonomous battery swapping. The speed of battery swapping has increased by 22%, with the fastest swapping taking only 2 minutes and 24 seconds. The battery compartment capacity has also been increased to 23 slots, with a maximum daily service capacity of up to 480 swaps.
NIO’s CEO Li Bin and Vice President Shen Fei have repeatedly stated publicly that "battery swapping is not a burden for NIO, the losses from battery swapping service are limited," "a single battery swapping station can achieve profitability with only 60 swaps per day," and "some investors are interested in NIO Power's independent financing, and the possibility of NIO Power's independent financing will not be ruled out in the future."
NIO’s "chargeable, swappable, upgradeable" energy service system is now widely recognized as NIO’s moat. The battery swapping mode is not only the service experience that consumers value most, but also a business model with huge market potential.
NIO continues to build on its strengths. In December of last year, Li Bin conducted a live test of the long-awaited 150kWh battery pack, driving from Shanghai to Xiamen, covering 1,044 km in 14 hours, providing strong evidence of the battery's capabilities.
To ensure user satisfaction with battery swaps and to avoid the negative emotions associated with swapping to older batteries, NIO’s battery swapping stations perform a health check on each battery during a swap. If a battery is found to be in an unhealthy condition, the station will take it out of service and replace it with a new one.
Moreover, in order to continually update healthy battery packs and further address the cost issues associated with short-lived batteries, NIO has implemented strategies to extend battery life and reduce the frequency of battery replacement, thereby reducing costs.
On March 14, 2024, NIO signed a framework agreement with CATL in Beijing to promote research and innovation of long-life batteries based on NIO’s battery swapping scenarios. Notably, the partnership has set a clear goal: to achieve a 15-year battery life with a health level still above 85%. If NIO and CATL succeed in achieving this goal, it will undoubtedly be a significant step forward for the new energy vehicle industry.









