CATL is planting another flag in Chongqing.
A new entity, CATL-Changan EV Battery (Chongqing) Co., Ltd., recently registered and received its business license. With a registered capital of 1 billion yuan, the company is wholly owned by CATL-Changan EV Battery Co., Ltd.—a joint venture between CATL and Changan Automobile.
As the global battery giant deepens its presence in this southwest industrial hub, its ties with the local automotive supply chain are tightening. But what is driving this strategy?
Deepening the JV: CATL-Changan EV Battery's "Chongqing Chapter"
CATL-Changan EV Battery (Chongqing) Power Battery Co., Ltd. did not emerge from a vacuum. Its parent, CATL-Changan EV Battery Co., Ltd., is itself the product of deep collaboration between CATL and Changan Automobile.
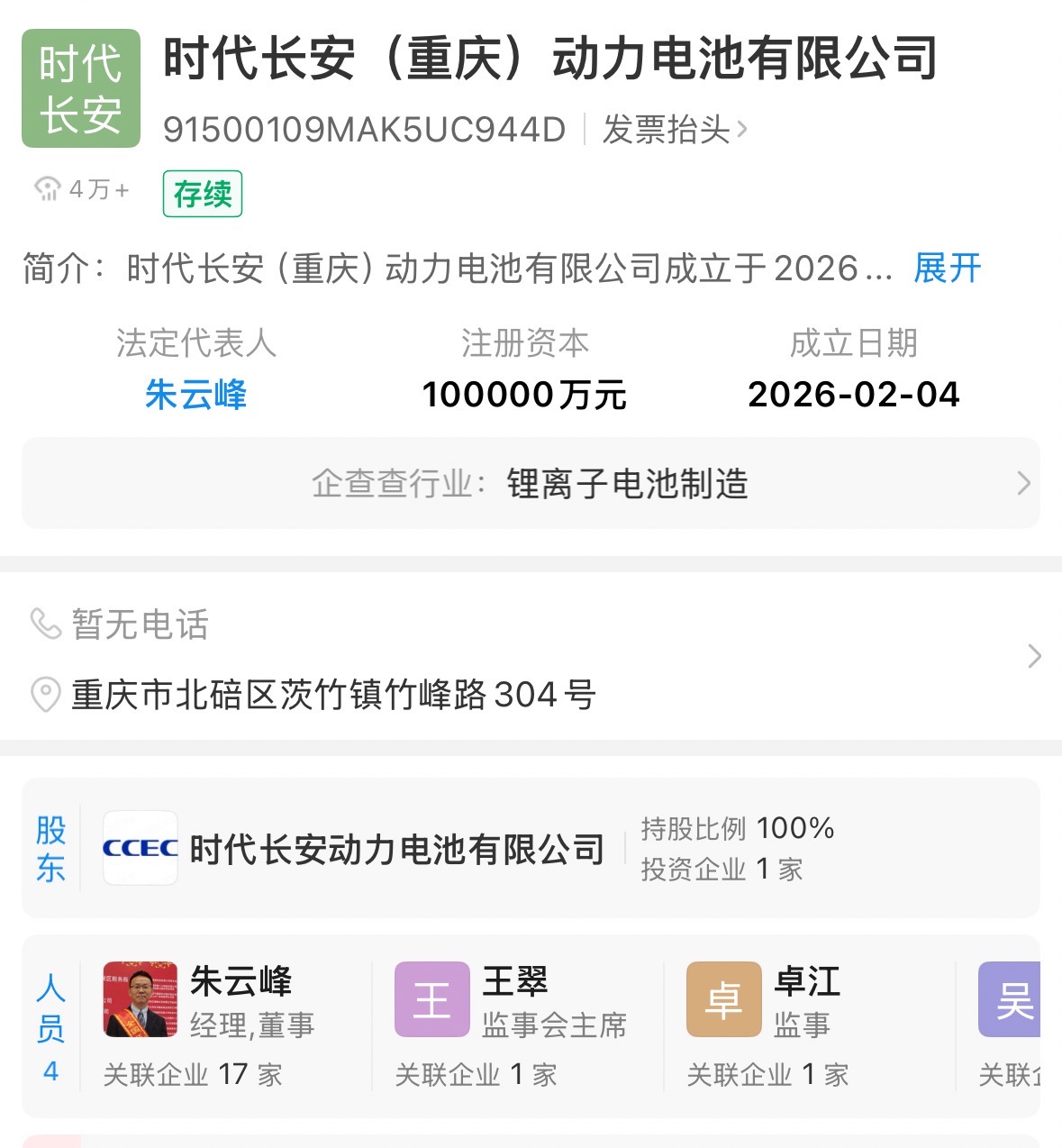
Image Source: Qichacha
Established in June 2023, the parent company is held by CATL, Deepal Automotive Technology Co., Ltd., and Changan Automobile Co., Ltd., representing the crystallization of their strategic alliance.
On January 14, 2026, the CATL-Changan EV Battery project was officially signed, settling in the Beibei section of the Chuan-Yu Gaozhu New Area. This major project involves a total investment of about 5.5 billion yuan and covers approximately 66.7 hectares. It will build a new 25 GWh power battery production base. Positioned as a "technology-leading new energy power battery support base," it is set to introduce CATL's latest generation battery processes—technologies that are both cutting-edge and compatible with future iterations.
Construction is scheduled to begin in the first quarter of 2026, with production slated to start in the second half of 2027. The goal is to reach full capacity within three years of launch. Once fully operational, the project is expected to generate an annual output value of about 10 billion yuan, contribute 300 million yuan in annual comprehensive tax, and create roughly 2,500 direct jobs.
Looking ahead, CATL's strategic intent in Chongqing is clear:
First, proximity to core markets. Chongqing and the broader Southwest region are traditional bastions of China's auto industry, where new energy vehicle production has surged in recent years. Localizing production drastically shortens supply chain response times and slashes logistics costs, allowing for agile responses to core client demands.
Second, locking in strategic customers. By establishing deep joint ventures and partnerships with local giants—specifically Changan Automobile and Seres Group (AITO)—CATL has effectively secured massive, guaranteed orders from these players for years to come. Against a backdrop of structural overcapacity and intensifying competition, binding top-tier automakers is crucial to maintaining market leadership.
Third, closing the regional ecosystem loop. From R&D to manufacturing (at the Qijiang base and the new CATL-Changan EV Battery facility) and direct supply (to Changan, Seres, etc.), CATL is building a full lifecycle ecosystem in Chongqing that integrates technology incubation, high-end manufacturing, and localized supply. This not only strengthens its own competitiveness in the Southwest but also significantly boosts the resilience, technological content, and value-added of the local automotive chain.
Tech Foresight: Paving the Way for Sodium-ion Batteries?
The emergence of CATL-Changan EV Battery (Chongqing) coincides with a pivotal moment in battery technology.
On February 5, Changan Automobile and CATL jointly hosted the "Changan Tianshu Intelligent New Safety Achievement Release and Sodium Battery Strategy Global Launch" in Yakeshi.
At the event, Changan unveiled its global sodium-ion strategy and debuted the world's first mass-produced sodium-ion passenger vehicle. The model has completed winter calibration in harsh cold environments, with its range, low-temperature performance, safety, and discharge capabilities all meeting practical standards.
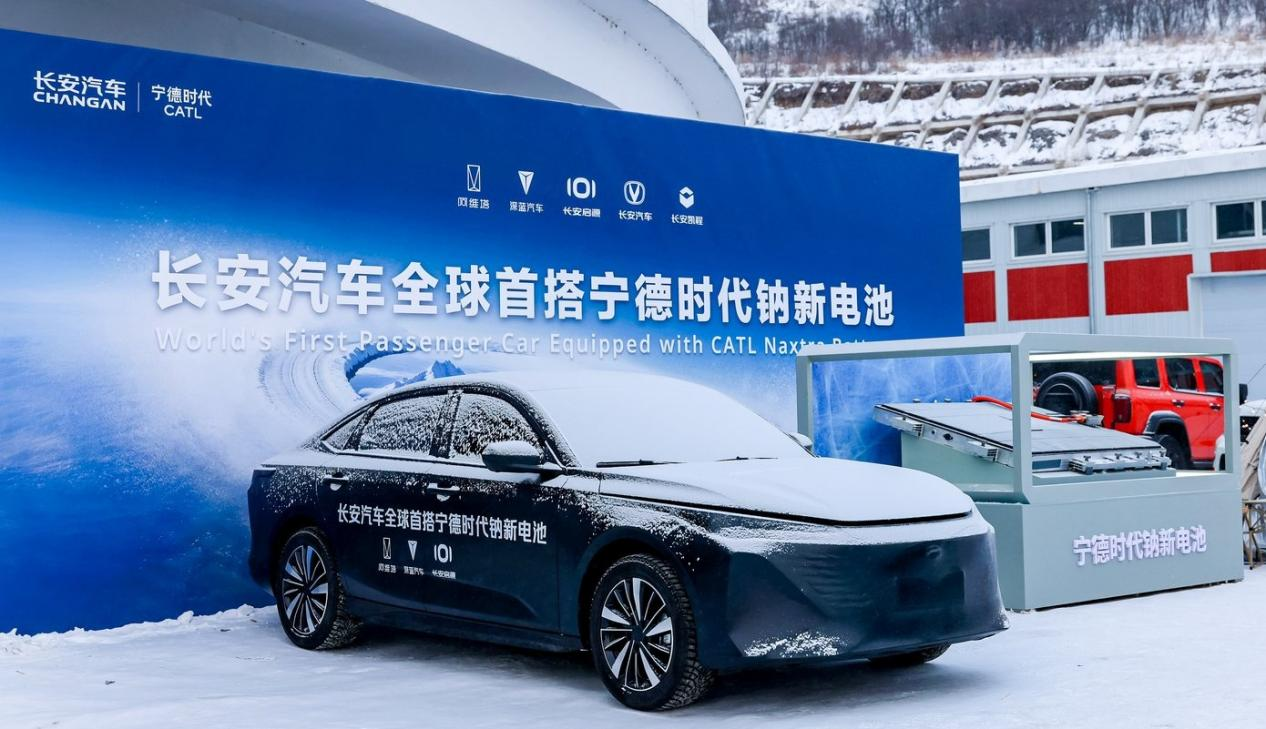

Image Source: CATL
Changan announced that its Avatr, Deepal, NEVO, and UNI brands will all feature sodium-ion batteries supplied by CATL in the future.
This partnership leaves significant room for the CATL-Changan EV Battery base's future product roadmap. While initial production may focus on advanced lithium-ion batteries, the planning and process compatibility allow for a rapid pivot to sodium-ion battery manufacturing down the line.
Sodium-ion batteries are seen as a vital complement to the lithium-ion system and a key future technology route, thanks to their abundant raw materials, cost potential, superior low-temperature performance, and high safety.
Changan has set an ambitious target: reaching 5 million units in annual production and sales by 2030, with new energy vehicles accounting for over 60% of that total. Achieving this will require support from diversified, low-cost, and high-performance battery technologies.
In essence, the CATL-Changan EV Battery Chongqing base is not merely a capacity add-on; it is likely a strategic stronghold for CATL and Changan to jointly mass-produce next-generation battery technologies—particularly sodium-ion batteries.
Consequently, CATL's renewed bet on Chongqing goes far beyond simple capacity expansion. This binding transcends the traditional buyer-seller relationship, evolving into a community with a shared future, involving shared risks, shared benefits, and joint R&D.
For Chongqing, CATL's sustained investment reinforces its status as a key intelligent connected new energy vehicle cluster in China and globally. For Changan, it secures a stable, cutting-edge, and cost-competitive "battery heart." And for CATL, it cements market barriers, locks in long-term orders, and paves a golden path for the industrialization of future technologies.









